Understanding Digital Accessibility Needs in K-12 Education
Identifying and addressing digital accessibility challenges in instructional technologies for youth with disabilities
The K-12 Education Working Group within the Maryland Initiative for Digital Accessibility (MIDA) is exploring the accessibility needs of K-12 students with disabilities, focusing on both assistive technologies (AT) and digital accessibility in instructional environments. Our aim is to support teachers, parents, and students by making digital educational tools more inclusive and effective for everyone. This project received seed funding through the MIDA Grand Challenges Impact Award.
Project Team: Gulnoza Yakubova; Beth Bonsignore; Yewon Lee; Amelia Gibson; Amy D’Agati; Dinesh Kumar Nanduri
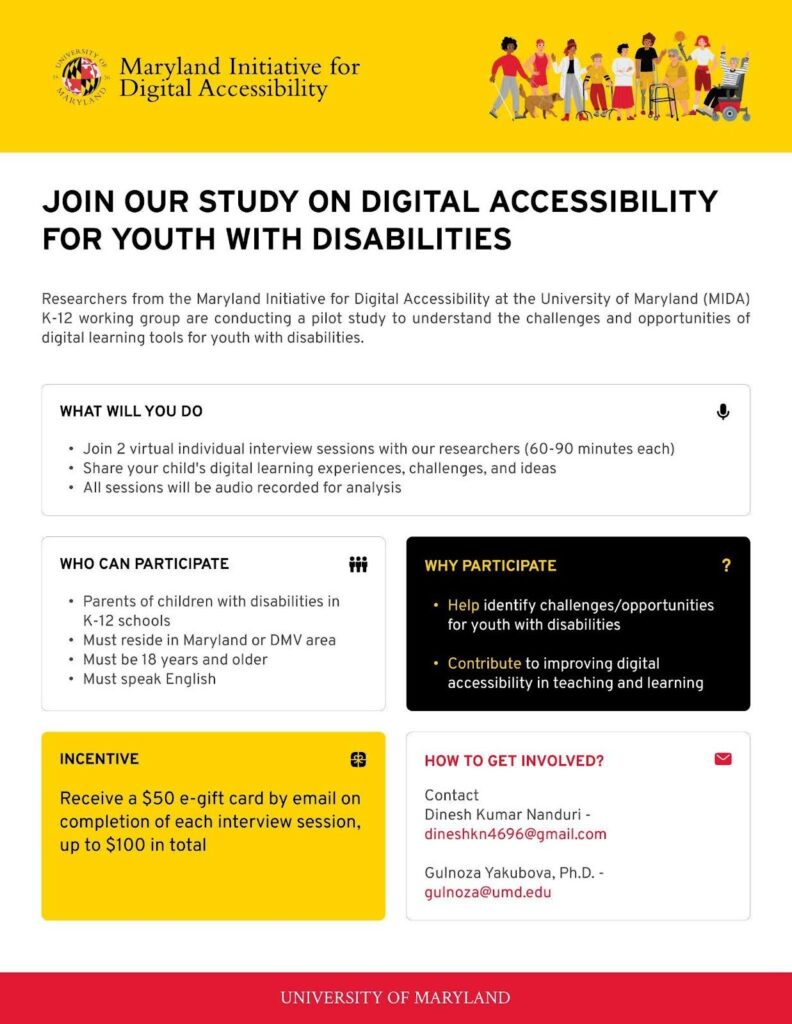
This study involves interviews with parents and educators to understand everyday barriers faced by youth with disabilities in digital learning environments and identify opportunities for improving digital accessibility in K-12 education.
Potential impact of this project on the lives of people with disabilities
Most youth with disabilities use digital technologies, including instructional technologies such as educational apps and learning management systems (LMS), to support their learning, growth and independence. These tools, used both in schools (formal learning) and at home (informal learning), include online classrooms, educational games and digital worksheets. However, they are often not designed to meet the specific needs of students with disabilities. The WCAG2.1 accessibility standards have improved accessibility for adults, but not for youth, leaving significant gaps in inclusive digital learning experiences. This might reinforce incorrect beliefs about the abilities of students with disabilities.
This project will help make the following outcomes possible:
- Understand Barriers: Identify the everyday barriers faced by youth with disabilities when using educational technologies.
- Inform a Workshop: Develop design options and features for at least one of the identified needs in digital accessibility.
Understanding these challenges is crucial for creating more inclusive digital learning environments, ultimately empowering youth with disabilities to fully engage and succeed in both formal and informal educational settings.
To accomplish the aims of this work, we are collaborating with We are doing this work in collaboration with DSA (Down Syndrome Association of Southern Maryland), LBPD (Maryland State Library for the Blind & Print Disabled), MDOD (Maryland Department of Disabilities), and Maryland School for the Blind.
Definitions
- Digital Accessibility: Making sure online content and tools (like websites, apps, and videos) are designed so that everyone, including people with disabilities, can use them easily and effectively.
- Assistive Technology (AT): Tools or systems used by individuals with disabilities to perform tasks that might otherwise be difficult or impossible.
- Instructional Technologies: Digital tools and platforms used in educational settings, including learning management systems and educational software.
- WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines): An international standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that provides specific guidelines for making web content accessible to people with disabilities. WCAG 2.1, the current version, includes requirements for features like:
- Text alternatives for images
- Captions for videos
- Sufficient color contrast
- Keyboard navigation
- Screener reader compatibility